Problem: Calculate the atomic mass of silver if silver has 2 naturally occurring isotopes with the following masses and natural abundances: Ag-107 106.90509 amu 51.84% Ag-109 108.90476 amu 48.46% A) 108.19 amu B) 107.90 amu C) 108.32 amu D) 108.00 amu E) 107.79 amu. Relative Atomic Mass of Silver The formula for relative atomic mass is the relative abundance over 100 divided by the isotope number. This can be expressed as: (A/100. a) + (B/100. b) + (C/100. c). = relative atomic mass.
The atomic mass unit (u) is defined as a mass equivalent to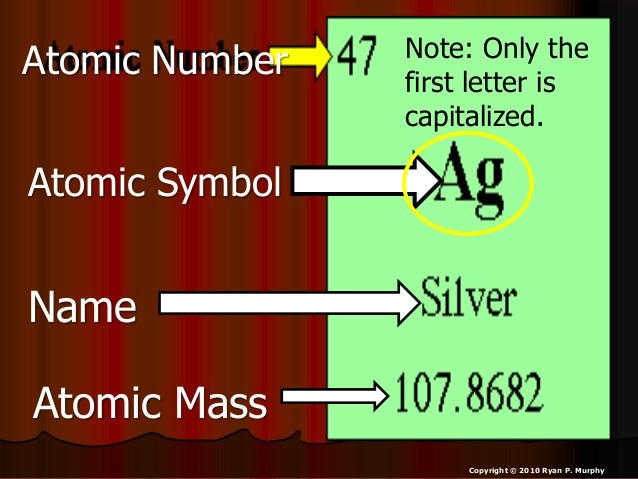
Molecular mass (molecular weight) is the mass of one molecule of a substance and is expressed in the unified atomic mass units (u). (1 u is equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12) Molar mass (molar weight) is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in g/mol. Weights of atoms and isotopes are from NIST article. ››More information on molar mass and molecular weight. In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all.
1/12 of the mass of one atom of carbon-12.1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
We can estmate the the relative atomic mass (atomic weight) of an element E with the naturally occurring isotopes aE, bE, c E, etc, and with the respective abundances of A%, B%, C% etc,
E, etc, and with the respective abundances of A%, B%, C% etc, | relative atomic mass (r.a.m.) | = ( | A 100 | × a) | + ( | B 100 | × b) | + ( | C 100 | × c) | + etc |
 Given the relative atomic mass (r.a.m.) of an element and the estimated mass of each of its isotopes, we can then estimate the relative abundance of each isotope: let x = %abundance of isotope-a
Given the relative atomic mass (r.a.m.) of an element and the estimated mass of each of its isotopes, we can then estimate the relative abundance of each isotope: let x = %abundance of isotope-a and 100 - x = %abundance of isotope-b
then, let r.a.m = relative atomic mass of the element:
| r.a.m. | = ( | x 100 | × mass isotope-a) | + ( | 100 - x 100 | × mass isotope-b) |
and solve for x

Molar Mass, Molecular Weight and Elemental Composition Calculator
Molar mass of Ag is 107.86820 ± 0.00020 g/mol Compound name is silver Convert between Ag weight and moles
Elemental composition of Ag
Sample reactions for Ag
Formula in Hill system is Ag | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Computing molar mass (molar weight)To calculate molar mass of a chemical compound enter its formula and click 'Compute'. In chemical formula you may use:
Molar mass calculator also displays common compound name, Hill formula, elemental composition, mass percent composition, atomic percent compositions and allows to convert from weight to number of moles and vice versa. Computing molecular weight (molecular mass)To calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound enter it's formula, specify its isotope mass number after each element in square brackets.Examples of molecular weight computations: C[14]O[16]2, S[34]O[16]2. Definitions of molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass and molar weight
Give us feedback about your experience with Molecular Weight Calculator. Related: Molecular weights of amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| molecular weights calculated today | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atomic Mass Of Ag
| Back to Online Chemical Tools Menu |
Atomic Mass Of Silver Chloride
© 2021 webqc.org All rights reserved
| Periodic table |
| Unit converters |
| Chemistry tools |
| Chemical Forum |
| Chemistry FAQ |
| Constants |
| Symmetry |
| Chemistry links |
| Link to us |
| Contact us |
How to cite? |
WebQC.Org online education free homework help chemistry problems questions and answers |
